blog: add cloud-init post
Signed-off-by: Christine Dodrill <me@christine.website>
This commit is contained in:
parent
040a53f065
commit
57d55213bc
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,480 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: My Magical Adventure With cloud-init
|
||||
date: 2021-06-04
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# My Magical Adventure With cloud-init
|
||||
|
||||
> "If I had a world of my own, everything would be nonsense. Nothing would be
|
||||
> what it is, because everything would be what it isn't. And contrary wise, what
|
||||
> is, it wouldn't be. And what it wouldn't be, it would. You see?"
|
||||
|
||||
- The Mad Hatter, Alice's Adventures in Wonderland
|
||||
|
||||
The modern cloud is a magical experience. You take a template, give it some SSH
|
||||
keys and maybe some user-data and then you have a server running somewhere. This
|
||||
is all powered by a tool called [cloud-init](https://cloud-init.io/). cloud-init
|
||||
is the most useful in actual datacenters with proper metadata services, but what
|
||||
if you aren't in a datacenter with a metadata service?
|
||||
|
||||
Recently I wanted to test a
|
||||
[script](https://github.com/tailscale/tailscale/blob/main/scripts/installer.sh)
|
||||
a coworker wrote that allows users to automatically install Tailscale on every
|
||||
distro and version Tailscale supports. I wanted to try and avoid having to
|
||||
install each version of every distribution manually, so I started looking for
|
||||
options.
|
||||
|
||||
[This may seem like overkill (and at some level it probably is), however as a
|
||||
side effect of going through this song and dance you can spin up a bunch of VMs
|
||||
pretty easily. <br /> <center> <blockquote class="twitter-tweet"><p lang="und"
|
||||
dir="ltr"><a
|
||||
href="https://t.co/yays27Wmes">pic.twitter.com/yays27Wmes</a></p>— Xe from
|
||||
Within (@theprincessxena) <a
|
||||
href="https://twitter.com/theprincessxena/status/1394265890494062593?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw">May
|
||||
17, 2021</a></blockquote> <script async
|
||||
src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js"
|
||||
charset="utf-8"></script> <center>](conversation://Mara/hacker)
|
||||
|
||||
cloud-init has a feature called the
|
||||
[NoCloud](https://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/topics/datasources/nocloud.html)
|
||||
data source. To use it, you need to write two yaml files, put them into a
|
||||
specially named ISO file and then mount it to the virtual machine. cloud-init
|
||||
will then pick up your configuration data and apply it.
|
||||
|
||||
[Wait...really? What.](conversation://Mara/hmm)
|
||||
|
||||
[Yes, really.](conversation://Cadey/coffee)
|
||||
|
||||
Let's make an [Amazon Linux
|
||||
2](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/amazon-linux-2-virtual-machine.html)
|
||||
virtual machine as an example. Amazon offers their Linux distribution for
|
||||
download so you can run it on-premises (I don't really know why you'd want to do
|
||||
this outside of testing stuff on Amazon Linux). In this blog we use KVM, so keep
|
||||
that in mind when you set things up yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
First you need to make a `meta-data` file, this will contain the VM's hostname
|
||||
and the "instance ID" (this makes sense in cloud contexts however you can use
|
||||
whatever you want):
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
local-hostname: mayhem
|
||||
instance-id: 31337
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[You can configure networking settings here, but our VM is going to get an
|
||||
address over DHCP so you don't really need to care about that in this case](conversation://Mara/hacker)
|
||||
|
||||
Next you need to make a `user-data` file, this will actually configure your VM:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
#cloud-config
|
||||
#vim:syntax=yaml
|
||||
|
||||
cloud_config_modules:
|
||||
- runcmd
|
||||
|
||||
cloud_final_modules:
|
||||
- [users-groups, always]
|
||||
- [scripts-user, once-per-instance]
|
||||
|
||||
users:
|
||||
- name: xe
|
||||
groups: [ wheel ]
|
||||
sudo: [ "ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL" ]
|
||||
shell: /bin/bash
|
||||
ssh-authorized-keys:
|
||||
- ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIPYr9hiLtDHgd6lZDgQMkJzvYeAXmePOrgFaWHAjJvNU cadey@ontos
|
||||
|
||||
write_files:
|
||||
- path: /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/80_disable_network_after_firstboot.cfg
|
||||
content: |
|
||||
# Disable network configuration after first boot
|
||||
network:
|
||||
config: disabled
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to change the username and swap out the SSH key as needed,
|
||||
unless you want to get locked out of your VM. For more information about what
|
||||
you can do from cloud-init, see the list of modules
|
||||
[here](http://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/topics/modules.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have the two yaml files you can make the seed image with this
|
||||
command (Linux):
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ genisoimage -output seed.iso \
|
||||
-volid cidata \
|
||||
-joliet \
|
||||
-rock \
|
||||
user-data meta-data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[In NixOS you may need to run it inside nix-shell: `nix-shell -p
|
||||
cdrkit`.](conversation://Mara/hacker)
|
||||
|
||||
Or this command (macOS):
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ hdiutil makehybrid \
|
||||
-o seed.iso \
|
||||
-hfs \
|
||||
-joliet \
|
||||
-iso \
|
||||
-default-volume-name cidata \
|
||||
user-data meta-data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can download the KVM image from that [Amazon Linux User Guide page from
|
||||
earlier](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/amazon-linux-2-virtual-machine.html)
|
||||
and then put it somewhere safe. This image will be written into a [ZFS
|
||||
zvol](https://pthree.org/2012/12/21/zfs-administration-part-xiv-zvols/). To find
|
||||
out how big the zvol needs to be, you can use `qemu-img info`:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ qemu-img info amzn2-kvm-2.0.20210427.0-x86_64.xfs.gpt.qcow2
|
||||
image: amzn2-kvm-2.0.20210427.0-x86_64.xfs.gpt.qcow2
|
||||
file format: qcow2
|
||||
virtual size: 25 GiB (26843545600 bytes)
|
||||
disk size: 410 MiB
|
||||
cluster_size: 65536
|
||||
Format specific information:
|
||||
compat: 1.1
|
||||
compression type: zlib
|
||||
lazy refcounts: false
|
||||
refcount bits: 16
|
||||
corrupt: false
|
||||
extended l2: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The virtual disk image is 25 gigabytes, so you can create it with a command like
|
||||
this:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ sudo zfs create -V 25G rpool/safe/vms/mayhem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you use `qemu-img convert` to copy the image into the zvol:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ sudo qemu-img convert \
|
||||
-O raw \
|
||||
amzn2-kvm-2.0.20210427.0-x86_64.xfs.gpt.qcow2 \
|
||||
/dev/zvol/rpool/safe/vms/mayhem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't use ZFS you can make a layered disk using `qemu-img create`:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ qemu-img create \
|
||||
-f qcow2 \
|
||||
-o backing_file=amzn2-kvm-2.0.20210427.0-x86_64.xfs.gpt.qcow2 \
|
||||
mayhem.qcow2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
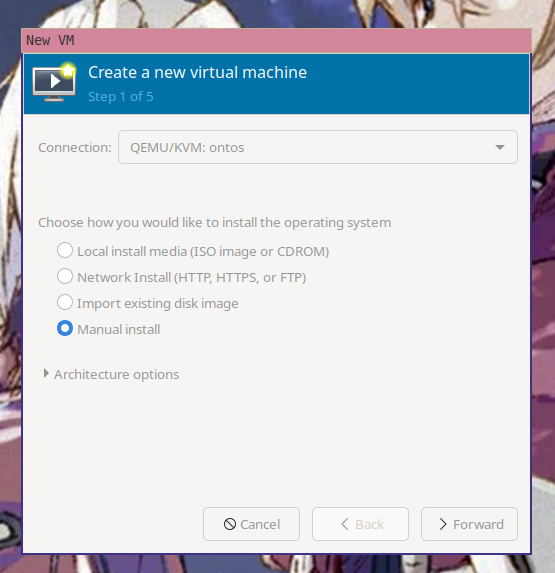
Open up virt-manager and then create a new virtual machine. Make sure you select
|
||||
"Manual install".
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
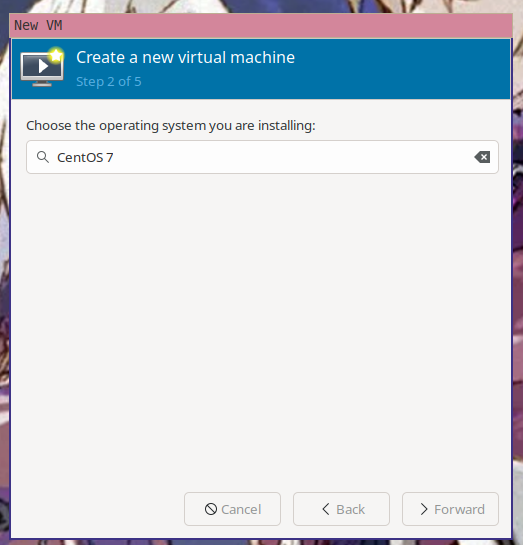
virt-manager will then ask you what OS the virtual machine is running so it can
|
||||
load some known working defaults. It doesn't have an option for Amazon Linux,
|
||||
but it's kinda sorta like CentOS 7, so enter CentOS 7 here.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
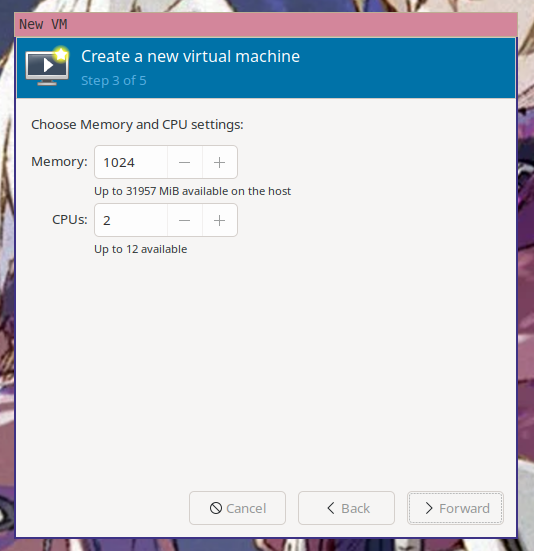
The default amount of ram and CPU are fine, but you can choose other options if
|
||||
you have more restrictive hardware requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
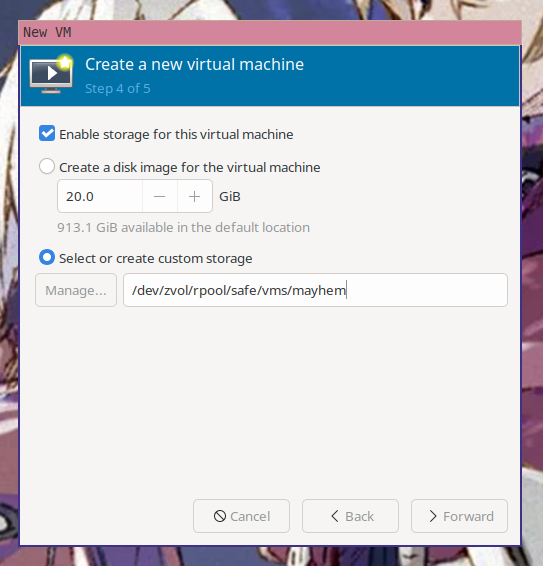
Now you need to select the storage path for the VM. virt-manager will helpfully
|
||||
offer to create a new virtual disk for you. You already made the disk with the
|
||||
above steps, so enter in `/dev/zvol/rpool/safe/vms/mayhem` (or the path to your
|
||||
custom layered qcow2 from the above `qemu-img create` command) as the disk
|
||||
location.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, name the VM and then choose "Customize configuration before install" so
|
||||
you can mount the seed data.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
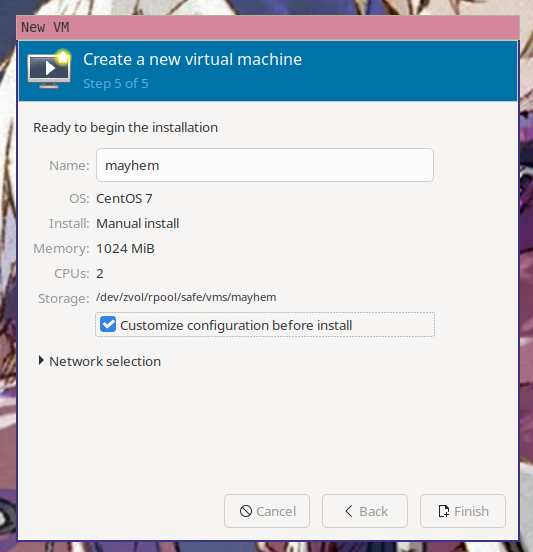
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
Click on the "Add Hardware" button in the lower left corner of the configuration
|
||||
window.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
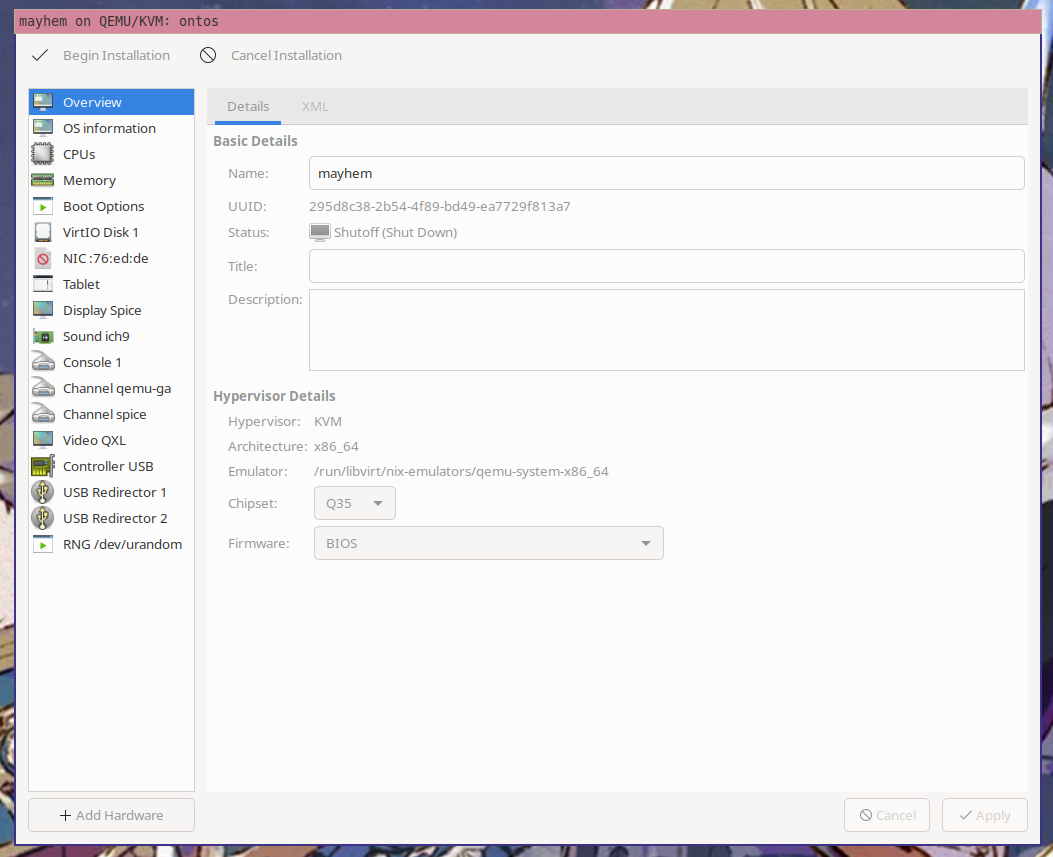
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
Make a new CDROM storage device that points to your seed image:
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
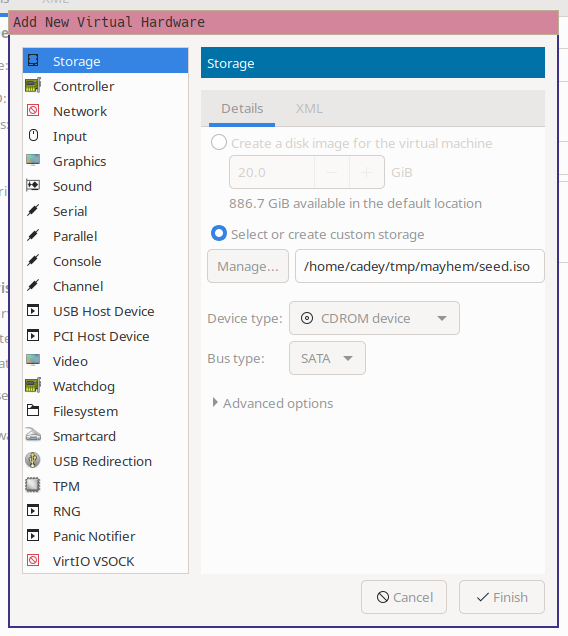
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
And then click "Begin Installation". The virtual machine will be created and its
|
||||
graphical console will open. Click on the info tab and then the NIC device. The
|
||||
VM's IP address will be listed:
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
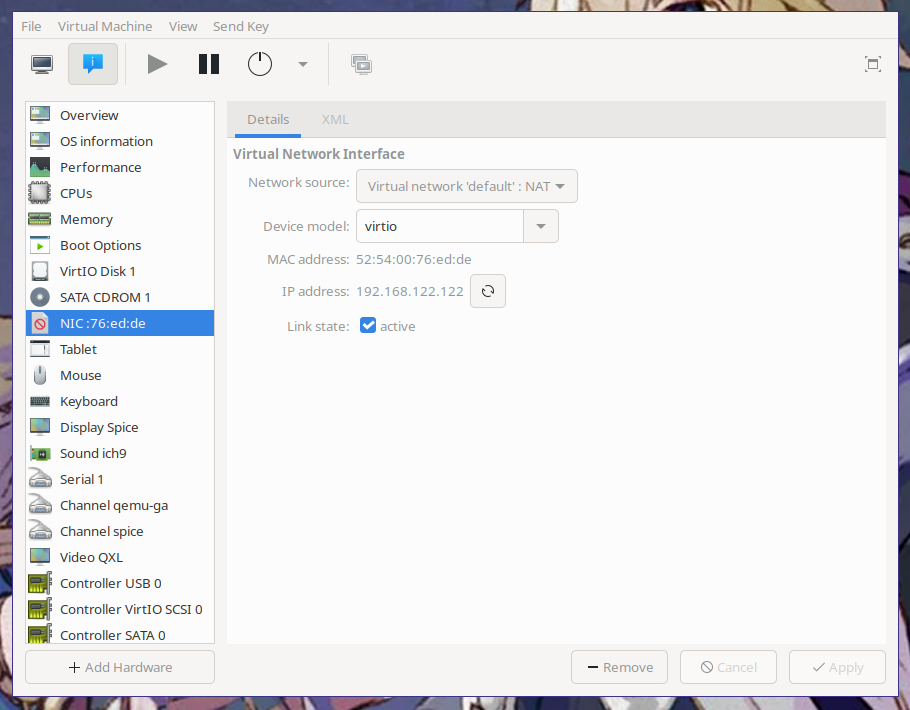
|
||||
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
Now SSH into the VM:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ ssh xe@192.168.122.122
|
||||
The authenticity of host '192.168.122.122 (192.168.122.122)' can't be established.
|
||||
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:TP7dWLkHOixx5tr78qn0yvDQKttH0yWz6IBvbadEqcs.
|
||||
This key is not known by any other names
|
||||
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
|
||||
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.122.122' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
__| __|_ )
|
||||
_| ( / Amazon Linux 2 AMI
|
||||
___|\___|___|
|
||||
|
||||
https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-2/
|
||||
8 package(s) needed for security, out of 17 available
|
||||
Run "sudo yum update" to apply all updates.
|
||||
[xe@mayhem ~]$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And voila! A new virtual machine that you can do whatever you want with, just
|
||||
like you would any other server.
|
||||
|
||||
[Do you really need to make an ISO file for this? Can't I just use HTTP like <a
|
||||
href="https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-instance-metadata.html">the
|
||||
AWS metadata service</a>?](conversation://Mara/hmm)
|
||||
|
||||
Yes and no. You can have the configuration loaded over HTTP/S, but without
|
||||
special network configuration you won't be able to have `http://169.254.169.254`
|
||||
work like the AWS metadata service without a fair bit of effort. Either way, you
|
||||
are going to have to edit the virtual machine's XML though.
|
||||
|
||||
[XML? Why is XML involved?](conversation://Mara/wat)
|
||||
|
||||
virt-manager is a frontend to [libvirt](https://libvirt.org/index.html). libvirt
|
||||
uses XML to describe virtual machines.
|
||||
[Here](https://gist.github.com/Xe/f870ebb2d9dce0929a35a4ba347cbda3) is the XML
|
||||
used to describe the VM you made earlier. This looks like a lot (because frankly
|
||||
it is a lot, computers are complicated), however this is a lot more manageable
|
||||
than the equivalent qemu flags.
|
||||
|
||||
[What do the qemu flags look like?](conversation://Mara/hmm)
|
||||
|
||||
[Like
|
||||
this](https://gist.githubusercontent.com/Xe/2eba35ec6cbd54becf9fca02f6d69f0b/raw/89d68424c0ae26333d798bd9bd6a224dfec844d7/qemu%2520flags.txt).
|
||||
It is kind of a mess that I would rather have something made by people smarter
|
||||
than me take care of.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable cloud-init to load over HTTP, you are going to have to add the qemu XML
|
||||
namespace to mayhem's configuration. At the top you should see a line that looks
|
||||
like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<domain type="kvm">
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replace it with one that looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<domain xmlns:qemu="http://libvirt.org/schemas/domain/qemu/1.0" type="kvm">
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will allow you to set the cloud-init seed location information using a
|
||||
[SMBIOS value](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/System_Management_BIOS). To enable
|
||||
this, add the following to the _bottom_ of your XML file, just before the
|
||||
closing `</domain>`:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<qemu:commandline>
|
||||
<qemu:arg value="-smbios"/>
|
||||
<qemu:arg value="type=1,serial=ds=nocloud-net;h=mayhem;s=http://10.77.2.22:8000/mayhem/"/>
|
||||
</qemu:commandline>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure the data is actually being served on that address. Here's a nix-shell
|
||||
python one-liner HTTP server:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ nix-shell -p python3 --run 'python -m http.server 8000'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will need to either load the base image back into the zvol or recreate
|
||||
the qcow2 file to reset the VM back to its default state.
|
||||
|
||||
Reboot the VM and wait for it to connect to your "metadata server":
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
192.168.122.122 - - [04/Jun/2021 11:41:10] "GET /mayhem/meta-data HTTP/1.1" 200 -
|
||||
192.168.122.122 - - [04/Jun/2021 11:41:10] "GET /mayhem/user-data HTTP/1.1" 200 -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can SSH into it like normal:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ ssh xe@192.168.122.122
|
||||
The authenticity of host '192.168.122.122 (192.168.122.122)' can't be established.
|
||||
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:eJRjDsvnVrXfntVtNVN6N+JdakaA+dvGKWWQP5OFkeA.
|
||||
This key is not known by any other names
|
||||
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
|
||||
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.122.122' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
__| __|_ )
|
||||
_| ( / Amazon Linux 2 AMI
|
||||
___|\___|___|
|
||||
|
||||
https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-2/
|
||||
8 package(s) needed for security, out of 17 available
|
||||
Run "sudo yum update" to apply all updates.
|
||||
[xe@mayhem ~]$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Can I choose other distros for this?](conversation://Mara/hmm)
|
||||
|
||||
Yep! Most distributions offer cloud-init enabled images. They may be hard to
|
||||
find, but they do exist. Here's some links that will help you with common
|
||||
distros:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Arch Linux](https://mirror.pkgbuild.com/images/) (use the `cloudimg` ones)
|
||||
- [CentOS 7](https://cloud.centos.org/centos/7/images/) (use the `GenericCloud`
|
||||
one)
|
||||
- [CentOS 8](https://cloud.centos.org/centos/8-stream/x86_64/images/) (use the
|
||||
`GenericCloud` one)
|
||||
- [Debian 9](http://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/OpenStack/9.13.22-20210531/)
|
||||
(use the `openstack` one)
|
||||
- [Debian 10](http://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/buster/20210329-591/) (use
|
||||
the `generic` one)
|
||||
- [Debian 11](http://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/bullseye/daily/) (use the
|
||||
`generic` one)
|
||||
- [Fedora 34](https://alt.fedoraproject.org/cloud/) (use the Openstack image)
|
||||
- [OpenSUSE Leap
|
||||
15.2](https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Cloud:/Images:/Leap_15.2/images/)
|
||||
(use the `OpenStack` image)
|
||||
- [OpenSUSE Leap 15.3](https://get.opensuse.org/leap/) (use the JeOS one labeled
|
||||
`OpenStack-Cloud`)
|
||||
- [OpenSUSE Tumbleweed](https://download.opensuse.org/tumbleweed/appliances/)
|
||||
(use the JeOS one labeled `Openstack-Cloud`)
|
||||
- [Ubuntu](https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/) (use the `server-cloudimg` image
|
||||
for your version of choice)
|
||||
|
||||
In general, look for images that are compatible with OpenStack. OpenStack uses
|
||||
cloud-init to configure virtual machines and the NoCloud data source you're using
|
||||
ships by default. It usually works out, except for cases like OpenSUSE Leap
|
||||
15.1. With Leap 15.1 you have to [pretend to be OpenStack a bit
|
||||
more](https://github.com/tailscale/tailscale/blob/aa6abc98f30df67a0d86698b77932d4d9cc45ac0/tstest/integration/vms/opensuse_leap_15_1_test.go)
|
||||
for some reason.
|
||||
|
||||
[What if I need to template the userdata file?](conversation://Mara/hmm)
|
||||
|
||||
[You really should avoid doing this if possible. Templating yaml is a delicate
|
||||
process fraught with danger. The error conditions in things like Kubernetes are
|
||||
that it does the wrong thing and you need to replace the service. The error
|
||||
condition with this is that you lose access to your
|
||||
server.](conversation://Cadey/facepalm)
|
||||
|
||||
[Let's say that Facts and Circumstances™ made me have to template
|
||||
it.](conversation://Mara/happy)
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source srcset="https://cdn.christine.website/file/christine-static/stickers/cadey/percussive-maintenance.avif" type="image/avif">
|
||||
<source srcset="https://cdn.christine.website/file/christine-static/stickers/cadey/percussive-maintenance.webp" type="image/webp">
|
||||
<img src="https://cdn.christine.website/file/christine-static/stickers/cadey/percussive-maintenance.png" alt="Cadey is percussive-maintenance">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
When you are templating yaml, you have to be really careful. It is very easy to
|
||||
incur [the wrath of Norway and
|
||||
Ontario](https://hitchdev.com/strictyaml/why/implicit-typing-removed/) on
|
||||
accident with yaml. Here are some rules of thumb (unfortunately gained from
|
||||
experience) to keep in mind:
|
||||
|
||||
- yaml has implicit typing, quote everything to be safe.
|
||||
- ensure that every value you pass in is yaml-safe
|
||||
- ensure that the indentation matches for every value
|
||||
|
||||
Something very important is to test the templating on a virtual machine image
|
||||
that you have a back door into. Otherwise you will be locked out. You can
|
||||
generally hack around it by adding `init=/bin/sh` in your kernel command line
|
||||
and changing your password from there.
|
||||
|
||||
When you mess it up you will need to get into the VM somehow and do one of a few
|
||||
things:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Run `cloud-init collect-logs` to generate a log tarball that you can export
|
||||
to your host machine and dig into from there
|
||||
2. Look through the system journal for any errors
|
||||
3. Look in `/var/log` for files that begin with `cloud-init` and page through
|
||||
them
|
||||
|
||||
If all else fails, start googling. If you are running commands against a VM with
|
||||
the `runcmd` feature of cloud-init, I'd suggest going through the steps on a
|
||||
manually installed virtual machine image at least once so you can be sure the
|
||||
steps work. I have lost 4 hours of time to this. Also keep in mind that in the
|
||||
context that `runcmd` runs from, there is no standard input hooked up. You will
|
||||
need to pass `-y` everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want a simple Alpine Linux image to test with, look
|
||||
[here](https://github.com/Xe/alpine-image) for the Alpine Linux images I test
|
||||
with. You can download this image from
|
||||
[here](https://xena.greedo.xeserv.us/pkg/alpine/img/alpine-edge-2021-05-18-cloud-init-within.qcow2)
|
||||
in case you trust that I wouldn't put malware in that image and don't want to
|
||||
make your own.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
In the future I plan to use cloud-init _extensively_ within my [new homelab
|
||||
cluster](https://twitter.com/theprincessxena/status/1400592778309115905). I have
|
||||
plans to make a custom VM management service I'm calling
|
||||
[waifud](https://github.com/Xe/waifud). I will write more on that as I have
|
||||
written the software. I currently have a minimum viable prototype of this tool
|
||||
called `mkvm` that I'm using today without any issues. I also will be writing up
|
||||
how I built the cluster and installed NixOS on all the systems in a future
|
||||
article.
|
||||
|
||||
cloud-init is an incredible achievement. It has its warts, but it being used in
|
||||
so many places enables you to make configuring virtual machines so much easier.
|
||||
It [even works on Windows!](https://cloudbase.it/cloudbase-init/). As much as I
|
||||
complain about it in this post, life would be so much worse without it. It
|
||||
allows me to use the magic of the cloud in my local virtual machines so I can
|
||||
get better use out of my hardware.
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue